超音波結合帶氧微氣泡誘發腫瘤血管正常化
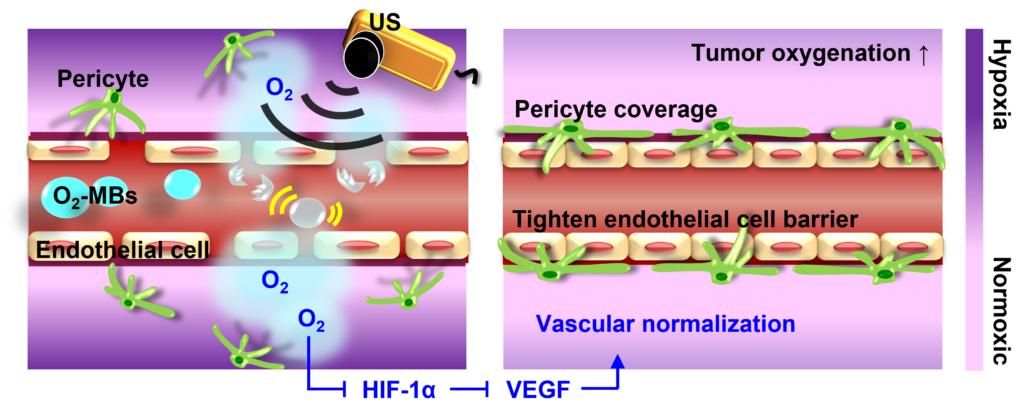
腫瘤生長與血管系統運送氧氣與養分息息相關,相較於正常組織的血管型態,腫瘤血管由於腫瘤細胞生長過密,加上血管新生因子的大量分泌,導致血管形態扭曲變形、部分功能缺失,無法有效運輸氧氣、養分與藥物,提升腫瘤缺氧、惡化與轉移機率,降低化學與放射治療的效果。近十年來,研究學者發現抗血管新生藥物可於特定時間內改變腫瘤血管型態,使其趨向正常化,有效提升氧氣與藥物的運輸效率,進而發展出腫瘤"血管正常化"之療法。然而腫瘤血管正常化具有時間窗的限制,只能於抗血管新生藥劑治療後的3-8天內提升治療效果,當時間窗一過,腫瘤血管新生會被過度抑制,缺氧區的擴大使腫瘤惡化並降低後續的治療效果,導致腫瘤血管正常化難以被運用在臨床治療上。因此,本研究提出使用超音波對比劑微氣泡,使其內部裝有氧氣,當超音波自體外刺激血液循環中的帶氧微氣泡時,可於腫瘤區域局部釋放氧氣,抑制血管新生因子因腫瘤缺氧而大量分泌的回饋機制,進而促使腫瘤血管正常化。由於此方法並非以化學藥劑抑制血管新生因子的表現與作用,有機會避免時間窗過後導致的腫瘤急性缺氧問題。本研究欲建立帶氧微氣泡治療下,腫瘤血管正常化之時間窗,與可誘發血管正常化之帶氧微氣泡劑量,並評估腫瘤血管正常化後,對於腫瘤微環境與藥物滲透之影響。
Normalization of tumor vasculature by oxygen microbubbles with ultrasound
Vascular normalization (VN) is proposed to remodel dysfunctional tumor vessels into normal and mature phenotype under anti-angiogenic status, which improves hypoxia and drug delivery in tumor therapy. However, tumor VN induced by anti-angiogenic agents (e.g. Avastin) only provides transient time window to limit clinical application in cancer therapy. Since angiogenesis is regulated by tumor hypoxia, promoting tumor oxygenation might be another pathway to accomplish VN. Therefore, our study investigated the feasibility of VN induced by oxygen-microbubbles (O2-MBs) with ultrasound. Homemade O2-MBs showed the O2 concentration of 8.90±0.02 mg/L. The prostate tumor-bearing mice were intravenously injected O2-MBs to locally release O2 within tumors by ultrasound sonication (2-MHz, 2 MPa, 1000 cycles, PRF of 2 Hz). Tumor perfusion was traced to define the time window of VN, which presented perfusion enhancement at 2-8 days after O2-MBs treatment. The expression of HIF-1α and VEGF reduced to 55±21% and 47±8%, respectively, which promoted pericyte coverage to improve vessel maturity (2.4±0.5-fold). These findings demonstrate that regulating tumor oxygenation by O2-MBs treatment could normalize dysfunctional vessels to enhance blood perfusion, vascular maturity, and drug accumulation.
Y.J. Ho, S.W. Chu, E.C. Liao, C.H. Fan, H.L. Chan, K.C. Wei, C.K. Yeh, “Normalization of Tumor Vasculature by Oxygen Microbubbles with Ultrasound”, Theranostics, 2019: 9, 7370-7383. (IF: 8.579, Categories: medicine, research & experimental: Rank: 10/139)